Your Guide to All 12 States Choosing Their Next Elections Chief in November
Candidates are debating how easy to make mail voting and direct democracy. And in some states, election deniers are still bidding to take over the system.
| September 16, 2024

One needs only to skim recent headlines to be reminded of the power of state elections officials to shape access to voting. Nebraska’s secretary of state just unilaterally shut down voter registration for tens of thousands of people with past felony convictions just weeks before the election. The secretary of state in Ohio, who has spent years courting the Big Lie, this month proposed to make it harder to vote by mail by limiting drop boxes. In Arizona, the secretary of state is laying the groundwork to combat election deniers who might seek to reject election results in November.
All these officials were elected by voters in the 2022 midterms, a busy cycle that saw a coordinated (and largely unsuccessful) effort by followers of Donald Trump to take over election administration. Two years later, a new round of states are selecting their chief election officials.
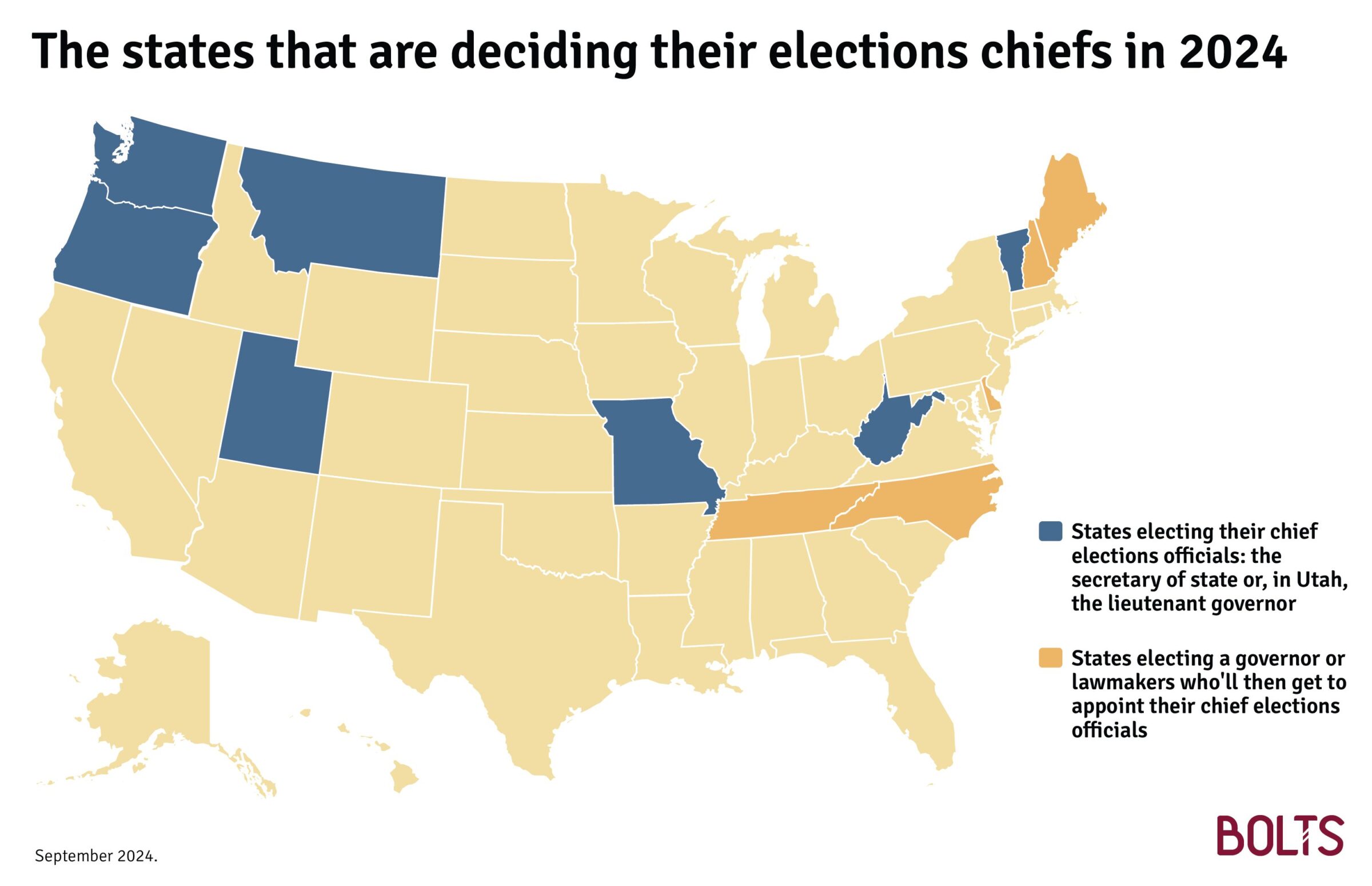
Twelve states are deciding in November who will run their elections going forward.
That role is directly on the ballot in seven states; in five others, voters will elect a governor or lawmakers who’ll then get to appoint their elections chief.
In most of these states, this elections chief is the secretary of state; but in a few, there is another office that has that authority—for instance, in Utah, it’s the lieutenant governor.
Today Bolts is publishing a new guide that walks you through these elections in all 12 states.
In some of these states, including Missouri, Oregon, and Vermont, a candidate is once again running who has clearly embraced false conspiracy theories that the 2020 election was stolen from Trump. They’ve proposed taking drastic actions such as ending mail-in voting.
In other states, such as New Hampshire or Utah, the office is unlikely to fall into the hands of an election denier. But even these races can be critical to the shape of democracy. Secretaries of state or the equivalent official often design voter outreach programs, or set policies that can make voter registration easy or difficult. They can also champion new election legislation or maneuver to stall ballot initiatives.
The exact roles that states attribute to their chief elections officials differ from state to state—for instance, some have a hand in election certification and others do not. To clarify this landscape, Bolts has published two databases. The first details, state by state, which offices prepare and administer an election (Who Runs our Elections?). The second details, state by state, which offices handle the counting, canvassing, and certification stages (Who Counts Our Elections?).
Explore our state breakdown of the 2024 elections below.
Delaware (via the governor’s race)
In Delaware, voters do not elect a secretary of state; instead, the governor appoints a state election commissioner. And voters this fall are choosing a new governor between New Castle County Executive Matt Meyer, a Democrat who is the heavy frontrunner in this blue state, and House Minority Leader Michael Ramone, a Republican.
The two candidates have taken very different stances toward election reforms. As a legislator, Ramone fought Democratic efforts to expand the availability of mail voting, while Meyer supported those changes. Meyer also says he would promote voting among some groups who are traditionally marginalized, vowing in response to an ACLU questionnaire to seek automatic registration of people exiting incarceration, and by expanding ballot access in local jails.
Maine (via legislative races)
Secretary of State Shenna Bellows, a Democrat, became a national figure in late 2023 when she took Trump’s name off of the state’s ballot, citing his support for an insurrection. (The U.S. Supreme Court later put Trump back on the ballot.) Whether the office changes hands next year depends on Maine’s legislative races: Lawmakers select a secretary of state every two years.
If Democrats retain the legislature, they could keep Bellows in office; Bellows told Bolts that she will seek another term. But the GOP has an outside shot at flipping the legislature in November. The last time they did that, in 2010, they replaced the Democratic secretary of state with a Republican. Democrats took back control of the legislature, and the secretary of state’s office, in 2012.

Missouri (via the race for secretary of state)
The secretary of state’s office in Missouri could fall into the hands of an ultraconservative Republican who has unambiguously embraced Trump’s lies about fraud and who vows that this would guide his tenure. “We have to ensure that none of the electoral fraud that took place in 2020 and stole the election from President Trump happens here,” Denny Hoskins, a state senator, told local media after winning a crowded GOP primary last month.
Hoskins, who is the front-runner in November in this staunch red state, has designs for major changes to election administration. He wants to hand count ballots and effectively eliminate absentee voting in an effort, his website says, to “root out election fraud and protect our elections from Chinese/Russian interference.”
He now faces Barbara Phifer, a Democratic state representative who broadly opposes his plans. She is also emphasizing her support for direct democracy, warning against GOP proposals to make it harder to pass citizen-initiated ballot initiatives. Hoskins championed such an effort this year, saying he was worried about the progressive push for an abortion rights measure.
Montana (via the race for secretary of state)
Secretary of State Christi Jacobsen, a Republican who is running for reelection, wants to make it harder for Montanans to vote. In 2021, her first year on the job, she strongly backed efforts by GOP lawmakers to toughen voter ID laws, end same-day registration, and make it more difficult to obtain an absentee ballot. Those policies were struck down earlier this year by the state’s liberal-leaning supreme court, and Jacobsen is now trying to get the conservative U.S. Supreme Court to revive them on appeal.
Jacobsen has also used her authority to stall ballot initiatives, recently blocking some signatures on petitions for measures to strengthen abortion rights and bring about election reforms.
Her Democratic opponent this November, Jesse James Mullen, says he is “appalled” by Jacobsen’s “efforts to disenfranchise Montanans.” Mullen, who owns a chain of local newspapers in Montana, opposes the GOP’s 2021 voting laws Jacobsen backed and criticizes Republicans for using false threats of voter fraud in Montana to justify new restrictions. Mullen will be an underdog in this red-leaning state that Trump is expected to decisively carry.
New Hampshire (via legislative races)
The secretary of state in New Hampshire is selected by lawmakers every two years, right after the state holds legislative elections. In the most recent such vote, in late 2022, Republican David Scanlan prevailed over a Democratic alternative. He benefited from the fact that the GOP narrowly controlled the state legislature but also got dozens of crossover votes from Democrats. That puts into question whether Democrats would oust Scanlan even if they take control of the legislature in November: In 2018, the most recent cycle in which Democrats won control of the legislature, just enough Democrats joined Republicans to reelect a secretary of state who had been supporting Republican restrictions on voter access.
Since becoming secretary of state in 2022, Scanlan has backed his party’s newest restrictions, including the proposal to require proof of citizenship when people want to register to vote.
North Carolina (via the governor’s race and/or legislative races)
While North Carolina is electing a secretary of state this year, this office has nothing to do with election administration. (For aficionados of secretary of state races, let the record reflect that longtime Democratic incumbent Elaine Marshall is seeking an eighth term against Republican Chad Brown, a county commissioner.)
Instead, it’s the gubernatorial and legislative races that’ll determine who controls the appointed offices that oversee elections: the state board of elections, and the director of elections.
But even then, it’s not clear who will have what power come 2025. Last year, in an ongoing effort to shrink the powers of their Democratic governor, North Carolina’s Republican lawmakers used their veto-proof majority to pass a new law stripping the governor of his influence over appointments and shifting more authority to the legislature. This was widely seen as a way to strip Democrats of their majority on the board and change the current director of elections, Karen Brinson Bell, who has questioned why the GOP is passing so many changes to election laws and has frustrated some conservatives who would like to see the state pursue fraud investigations more aggressively.
The new law is currently caught up in court, however. The stakes of the battle over appointment powers are high: Democrats and Republicans have been clashing on a wide range of voting issues in the state, including same-day voter registration and voter ID laws.
Oregon (via the race for secretary of state)
Oregon has frequently led the way in expanding ballot access, including by pioneering universal mail voting and automatic voter registration. Democrat Tobias Read, currently state treasurer, says he is running for secretary of state this year to uphold that tradition. “Any effort to make it easier for people to vote, to remove barriers, is a good thing,” he told Bolts earlier this year, ahead of his primary victory.
Read’s Republican opponent, state Senator Dennis Linthicum, could hardly be more different, as Bolts reported in May. He is proposing to ban mail voting, despite the fact that most of the state votes by mail. He joined far-right lawmakers nationwide in 2020 to call for an audit of the 2020 presidential election based on unsubstantiated claims of fraud. And he has not committed to certifying election results, the role of a secretary of state.
Read is favored to win this race; Oregonians haven’t elected any Republican to statewide office since 2016. That would leave Linthicum without an office. He was barred from seeking another term in the state Senate because he participated in a prolonged GOP statehouse walkout in 2023.

Tennessee (via legislative races)
The secretary of state in Tennessee is not directly elected. Instead, the legislature chooses a secretary of state, who then names a state coordinator of elections—and that’s the person who state law designates as Tennessee’s chief elections official.
Republicans are massively favored to retain both chambers of the state legislature, making it very unlikely that election administration will take a different route. Secretary of State Tre Hargett has been in office since 2009, and he easily secured a new four-year term in 2021.
Mark Goins, the elections coordinator appointed by Hargett back in 2009, acted last year to drastically shut down people’s ability to regain their right to vote after a felony conviction, imposing new financial fees to even apply, and making success an extremely tall order. Hargett and Goins have backed restrictions on voter registration and mail voting, and have opposed Democratic proposals to boost turnout.
Vermont (via the race for secretary of state)
In a rematch of the 2022 race, Secretary of State Sarah Copeland Hanzas, a Democrat, faces H. Brooke Paige, a perennial Republican candidate who has fully embraced Trump’s lies about the 2020 election. The Big Lie does not sell in blue Vermont: Copeland Hanzas won the 2022 election 61 percent to 33 percent. There’s no indication that 2024 will be any different.
“It is highly worrisome to hear people echoing false claims and misinformation about the safety and security of our elections,” Copeland Hanzas told Bolts two years ago. “It is a fundamental threat to our democracy, in that the purpose of these claims is to discourage people from participating in elections.”
Copeland Hanzas has supported efforts by some Vermont municipalities to expand the franchise locally. Bolts has reported, for instance, on the organizing that led several cities to allow noncitizen residents to participate in local elections on Town Hall days. “We heard from these communities about why they thought it was important to be able to welcome people into the democratic franchise at the local level,” Copeland Hanzas told Bolts on why she helped authorize those reforms while in the legislature.
Utah (via the race for lieutenant governor)
Utahns abolished their secretary of state’s office in 1976, transferring the authority to oversee elections to the lieutenant governor instead.
Lieutenant Governor Deidre Henderson, a Republican, is running for reelection this year. She barely survived the GOP primary against a conservative activist who had helped organized a ballot measure to restrict mail voting and voter access. During her first term, Henderson refused to leave a bipartisan election organization that’s come under conservative fire, saying she wouldn’t bow to “radical election deniers.”
In Utah’s general elections, lieutenant governors appear on a ticket with their running-mate as part of the governor’s race, so Henderson’s fate is tied to the race between Governor Spencer Cox and Democrats’ gubernatorial nominee Brian King, who is running on a ticket with Rebekah Cummings, a librarian at the University of Utah. In this staunchly red state, it’ll be an uphill climb for Democrats to land a statewide win.
Washington (via the race for secretary of state)
In 2022, a Democrat won the secretary of state’s office for the first time in a half-century. But that was in a special election, and Steve Hobbs now has to run for a full term against Republican Dale Whitaker, the former executive director of a conservative organization.
Whitaker, who associated himself with “America First grassroots patriots” at his state party’s convention, has taken issue with some of the state’s election rules. He has made public comments against the availability of mail voting, despite running in a state where voters trust and widely use mail ballots. “I will fight for same-day in-person voting with paper ballots,” he said in April. Hobbs supports the mail voting system. Whitaker has also taken issue with Hobbs’ decision, as part of the settlement of a lawsuit filed last year, to agree to a consent decree that removes a requirement that Washington residents wait 30 days to register to vote when they move to a new address. Whitaker, who said a “reasonable registration deadline” is important, did not reply to a request for comment on whether he supports the state’s same-day voter registration rules.
Hobbs received 48 percent in the August all-party primary, which is generally predictive of the November results, with another Democrat taking 10 percent. Whitaker received 37 percent, leaving him an underdog in November.
West Virginia (via the race for secretary of state)
West Virginia’s outgoing secretary of state, Republican Mac Warner, says the CIA robbed Trump of victory in 2020 and attended a “Stop the Steal” rally late that year. He unsuccessfully ran for governor this year. The favorite to replace him as secretary of state? His brother Kris Warner, who also refuses to call the 2020 results legitimate.
Kris Warner is currently the director of the state’s Economic Development Authority. As he runs to become West Virginia’s next top elections official, he’s promising to purge voter rolls and figures to fit neatly within a state Republican Party that has deeply embraced election denial.
His Democratic opponent, local attorney Thornton Cooper, has said he was motivated to run because he views the Warner brothers as particular threats to democracy. But it’s become very difficult for Democrats to win in West Virginia, and Cooper doesn’t seem to be trying much. He has no functioning campaign website as of publication and, according to the state’s data, he has spent under $2,000 on this race.

What about the remaining states?
Of the 38 states that aren’t on this list, the vast majority will hold elections for secretary of state, or an equivalent office, in 2026. (Check out Bolts’ national primer from 2022 for more on how many of these states’ elections unfolded last time around.) But before that, the next milestone looms in 2025: New Jersey and Virginia will host wide open governor’s races, and the two winners will get to select their state’s secretaries of state.
Sign up and stay up-to-date
Support us
Bolts is a non-profit newsroom that relies on donations, and it takes resources to produce this work. If you appreciate our value, become a monthly donor or make a contribution.



