What Off Year? Hundreds of Local Elections Will Define Criminal Justice Policy in 2023
Big-city mayor races and elections for prosecutor and sheriff—especially in Louisiana, Mississippi, New York, Pennsylvania and Virginia—will shape policing, punishment and jail conditions in 2023.
Daniel Nichanian | December 14, 2022


In 2022, voters largely defied expectations of a backlash against criminal justice reform. Progressives lost a figurehead as San Francisco recalled its district attorney but also added to the ranks of officials intent on reducing incarceration and abandoning the punitive status quo on criminal justice—from John Fetterman in Pennsylvania to Pam Price in California and Mary Moriarty in Minnesota. Now those debates will continue right into 2023, bringing in voters who didn’t get to weigh in this year.
Many states hold their local elections on odd-numbered years—a schedule that depresses turnout and that some places are fighting to change. That means that, if you’re interested in the shape of your criminal legal system, critical storylines are already taking shape: These local and state offices enjoy the brunt of the discretion to shape incarceration and policing. DAs and sheriffs, in particular, decide which cases to prosecute and with what severity, exercise nearly unfettered control over jail conditions, and choose how they partner with federal immigration enforcement.
There are nearly 500 elections for prosecutors and sheriffs scheduled for 2023, a Bolts analysis finds—and the first filing deadlines are coming up in just weeks.
These elections are largely concentrated in Louisiana, Mississippi, New York, Pennsylvania, and Virginia, with just a few sprinkled in Florida, New Jersey, and Washington State. (The full list is available here.)
Other local offices that shape criminal punishment and policing are also on the ballot next year, including three governorships, at least two supreme court justices in Pennsylvania and Wisconsin, and hundreds of state lawmakers, local judges, and mayors.
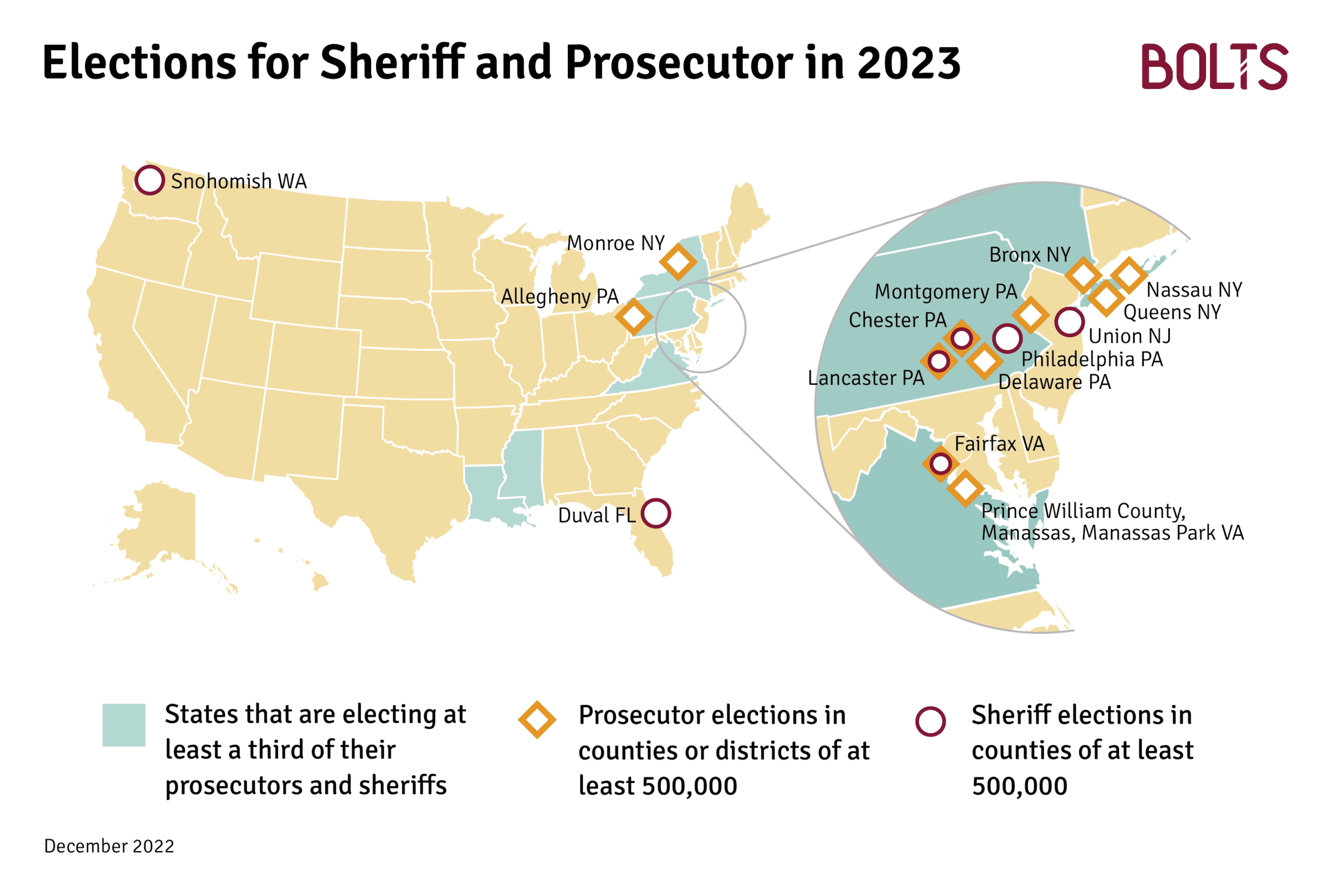

Local elections are often very late to take shape, so in most cases the field remains undefined. At this time, the likeliest elections to draw the stark contrasts we have seen in recent cycles—with candidates disagreeing on whether to intentionally aim to reduce incarceration, or what goes into advancing public safety—include prosecutor races in New York City and upstate New York, Pittsburgh and the Philly suburbs, and Northern Virginia, as well as mayoral races in Chicago, Philadelphia, Denver, and across Texas. Sheriff races across Louisiana, Mississippi, and Virginia may draw some scrutiny to immigration and detention conditions.
Bolts will follow these races throughout the year. Today, I am kicking off our coverage by laying out six big questions that will define the cycle:
1. Can reform-minded prosecutor candidates hold their ground in Virginia, and make inroads elsewhere?
The last time the counties that are electing their prosecutors in 2023 voted for these same officials, in 2019, the results made for a striking split screen. Virginia saw one of the widest set of wins to date for candidates who campaigned on reducing incarceration. After winning in a string of populous suburban counties, they formed a statewide coalition called Virginia Progressive Prosecutors for Justice—at the time an unprecedented step—that advocating for lawmakers to abolish the death penalty and mandatory minimums, among other reforms. But their positions drew heavy heat from the right, including judicial pushback and failed recalls as well as criticism from the left over false promises.
Now, those first-term incumbents are up for election again. They include Arlington’s Parisa Dehghani-Tafti and Fairfax’s Steve Descano, both in Northern Virginia, who drew attention in 2019 for ousting a pair of incumbents in Democratic primaries, as well as Albemarle’s James Hingeley, Loudoun’s Buta Biberaj, and Prince William’s Amy Ashworth. Several of these incumbents are now facing challengers, intra-party strife, or conservative anger, and the results of the 2023 cycle will determine the political strength of the state’s reform prosecutor coalition going forward.
In New York and Pennsylvania, though, the 2019 DA elections saw advocates of criminal justice reform largely stagnate due to the sky-high number of uncontested elections and some high-profile losses.
Pennsylvania’s marquee election in 2023 is likely to be the DA race in Allegheny County (Pittsburgh), where longtime Democratic DA Stephen Zappala is a vocal critic of criminal justice reforms amid significant racial disparities in his office. In 2019, Zappala beat multiple progressive challengers, though progressive organizers have made major progress in Pittsburgh in the intervening years, including winning a ballot measure meant to curtail solitary confinement and electing decarceral judges in 2021.
Other DA races in Pennsylvania include counties like Cumberland and Lancaster that took a distinctly punitive approach to the opioid crisis, and populous Philly suburbs like Chester, Delaware, and Montgomery. Philadelphia’s reform DA Larry Krasner is not up after cruising to re-election in 2021; he has remained relatively isolated so far among DAs in the state, a far cry from the dynamic in Virginia, and 2023 will be the next test of whether his allies can change that.
In New York, where most prosecutors have been relentlessly critical of a landmark package of pretrial reforms, at least two former presidents of the state’s DA association are up for re-election this year—in Monroe County (Rochester) and Onondaga County (Syracuse). Another DA who has battled against state Democrats’ bail reform, William Grady of Dutchess County (Poughkeepsie), has said he is retiring after 40 years as DA.
Bronx DA Darcel Clark has drawn a reform challenger who says she is running to “end mass incarceration” four years after securing re-election unopposed. Also on the 2023 calendar: Queens, the site of the extraordinarily tight 2019 race that saw Melinda Katz become DA after defeating socialist organizer Tiffany Cabán.
In Mississippi, I have my eyes on the Fifth District, which covers seven counties in the central part of the state: DA Doug Evans drew national opprobrium and condemnation from the U.S. Supreme court for his decadeslong effort to prosecute Curtis Flowers six times for the same crime—a crusade exposed in the podcast “In the Dark.” Even with that exceptional spotlight, Evans ran unopposed in 2019 and remains in office, with little accountability, today.
2. Will sheriffs and jailers face accountability?
The 2022 midterms showcased once again that, with some exceptions, sheriffs tend to secure re-election even when they link up in far-right networks, signal their eagerness to disrupt the federal government, or prepare to disrupt local elections. Next year will bring a different cast of characters to the forefront. There’s Sheriff Adam Fortney of Snohomish County, Washington, in the Seattle suburbs, who faced a recall effort in 2020 for quickly disregarding statewide COVID rules even while ramping up other arrests.
There’s Sheriff Sid Gautreaux, in East Baton Rouge, Louisiana’s most populous parish, who runs a jail with infamously dangerous conditions. Or there’s Sheriff Mike Chapman in Loudoun County, Virginia, who has drawn scrutiny for accepting campaign donations from private contractors that work with his office, a common practice among jailors. The vast majority of sheriffs in Louisiana and Virginia will be elected in 2023, creating a window for local jails to draw more public attention.
Note that Pennsylvania sheriffs have far more limited powers than elsewhere as they typically do not run local jails, which are managed directly or indirectly by other local offices, many of which are on the ballot in 2023. A string of deaths at the Allegheny County jail, located in Pittsburgh, and complaints that the lockup is violating a voter-approved ban on solitary confinement are now issues set to define the race for the county’s next chief executive.
3. Will immigrants’ rights advocates continue to curtail local collaboration with ICE?
When Donald Trump was president, voters in Democratic-leaning counties ousted public officials who cooperated with Immigration and Customs Enforcement. But ICE forged new relationships with Southern jails to make up for it, and sheriffs rushed to profit off renting vacant jail space for ICE to detain migrants and asylum-seekers. In 2023, nearly all sheriffs will be on the ballot in Louisiana and Mississippi, states that proved to be difficult terrain for critics of those ICE arrangements four years ago.
Still, immigrants’ rights advocates have opportunities in some blue-leaning areas to build on their 2022 successes and elect new officials who oppose collaborating with ICE.
Just four counties with 2023 sheriff races participate in ICE’s 287(g) program, which deputizes local law enforcement to act like federal immigration agents in jails. Three of them voted for Joe Biden over Trump: Duval County (Jacksonville), Florida; East Baton Rouge Parish (Baton Rouge), Louisiana; and Rensselaer County (Troy), New York. (The fourth, which voted for Trump, is Culpeper County, Virginia.)
Still, recent history suggests that efforts to curtail cooperation with ICE will be tricky in all three blue-leaning counties. Republicans defended the sheriff’s office in Duval in a special election just last month. In East Baton Rouge, the GOP sheriff easily prevailed in 2019 with endorsements from prominent Democratic officials. And in Rensselaer, the only county in all of New York State that’s part of the 287(g) program, the Republican incumbent ran entirely unopposed four years ago.
4. Will there be more interest in city halls to reform policing?
Since the Black Lives Matter protests of 2020, the most ambitious electoral platforms for changing or reducing policing have emerged at the municipal level—but so has the most stringent backlash. In the absence of federal elections, 2023 may be the year those dynamics again take front stage with many of the nation’s biggest cities set to hold mayoral races, including five cities of more than one million: Chicago, Dallas, Houston, Philadelphia, and San Antonio. Many others will vote for their city councils.
These elections will feature incumbents who have tended to clash with protesters, such as Chicago’s incumbent mayor Lori Lightfoot; Democrats with a tough-on-crime reputation, such as John Whitmire, a Texas state senator running for Houston mayor; and candidates who have championed shifting resources from policing to other social services, such as Leslie Herod, who is running for mayor in Denver, or Cabán and other left-leaning council members who are up for re-election in New York. Watch out for whatever contrasts emerge around police budgets and ordinances that criminalize homelessness.
5. Will reform initiatives survive state elections in the South?
In 2023, the elections that may change who runs state governments will largely be concentrated in the South, and the GOP has room to extend their power in what’s already their strongest region.
In Virginia, the GOP governor and attorney general’s tough-on-crime posturing have run into the Democratic-run state Senate, which has rejected the former’s appointments to the parole board and killed the latter’s proposal to crack down against the state’s reform prosecutors. Should they flip the Senate in 2023, the GOP would gain full control of the state government and could press forward on those matters.
In Kentucky, Democratic Governor Andy Beshear will seek a second term in difficult conditions given the state’s conservative bent. On his third day in office, he issued an executive order enabling hundreds of thousands of Kentuckians with felony convictions to vote; his re-election bid may decide the fate of his initiative since the GOP has reversed a similar one in the past.
The GOP also hopes to gain full control of Louisiana’s government; Democratic Governor John Bel Edwards cannot run for a third term, in a state where a short-lived bipartisan agreement to lower incarceration shattered within years of him signing a landmark reform package in 2017.
6. How will judicial elections shape criminal punishment in Pennsylvania and Wisconsin?
In 2021, Pittsburgh and Philadelphia progressives made the unusual choice of organizing around local judicial races, and it paid off with a wave of wins by candidates who ran on curtailing bail and reducing incarceration. Next year, there will be more elections for the local bench in both places.
Also in 2023, all Pennsylvanians will get to vote in a supreme court election to replace Max Baer, a Democratic justice who died this fall. The court, which is sure to retain a Democratic majority, has vacillated on criminal justice matters. One of Baer’s final opinions came in a September ruling that brought relief to defendants with mental illness, though the court has also disappointed reformers by rejecting cases challenging the death penalty or felony murder statutes.
While Pennsylvania’s election won’t be resolved until November, one of the year’s most important races looms in April: A state supreme court seat on the ballot in Wisconsin may hand the majority to the liberal wing. Such a flip would affect criminal justice cases that have long divided Wisconsin justices, but the fate of the state’s 1849 abortion ban also looms large. Wisconsin’s staunchly GOP legislature is locked into place by aggressive gerrymanders; unlike neighboring Michigan, there is no mechanism for citizens to put a popular initiative on the ballot. That leaves state litigation, and April’s judicial election, as a rare path for Wisconsinites to curtail the policing of reproductive rights.
Sign up and stay up-to-date
Support us
Bolts is a non-profit newsroom that relies on donations, and it takes resources to produce this work. If you appreciate our value, become a monthly donor or make a contribution.

