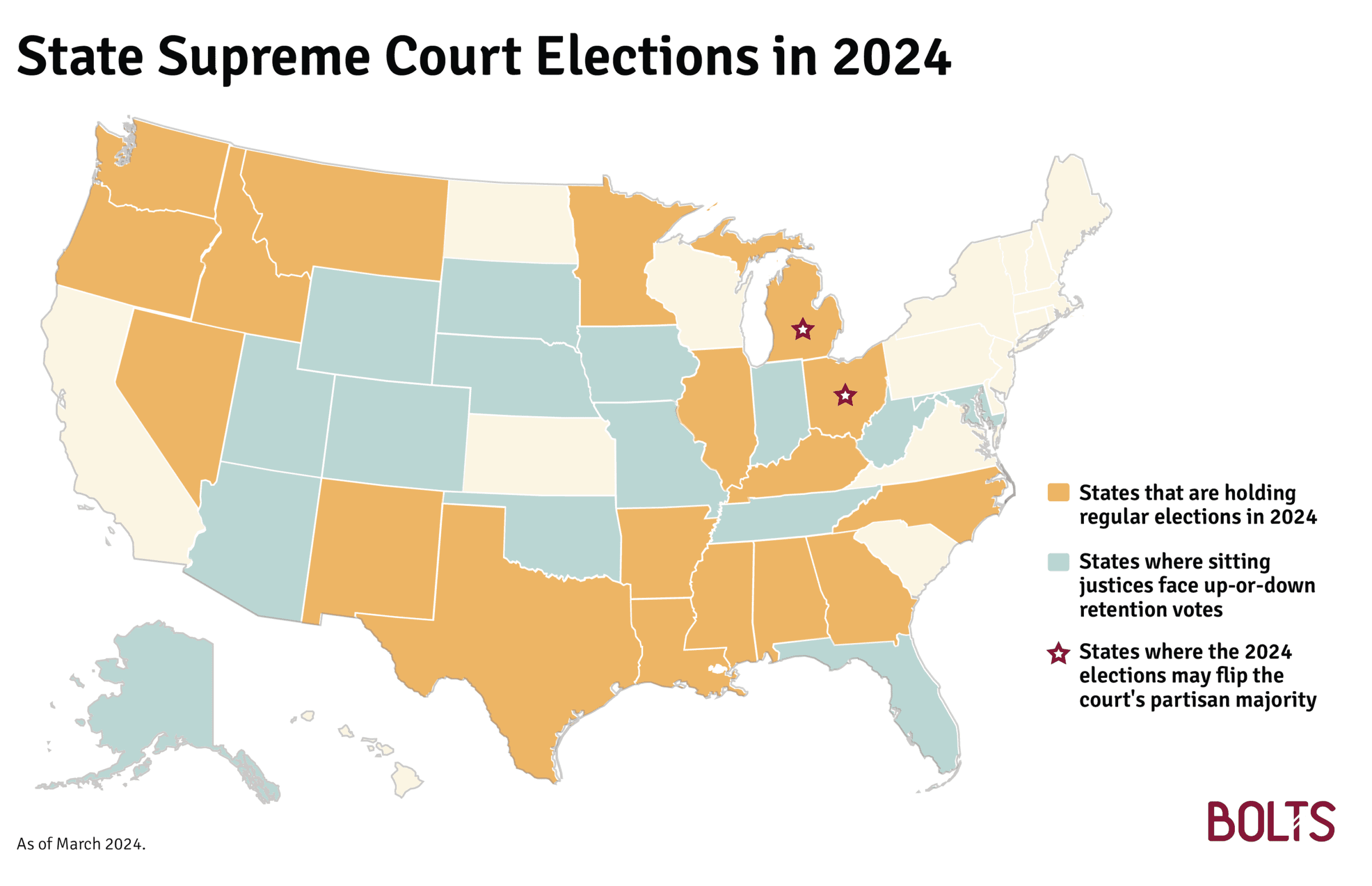
Your State-by-State Guide to the 2024 Supreme Court Elections
Voters this year are deciding the fate of 82 seats across 33 states’ high courts. Cases involving abortion, democracy, and other critical issues hang in the balance.
Daniel Nichanian | April 3, 2024


The Texas supreme court closed out 2023 by blocking an abortion during a medical emergency, forcing a woman to flee the state. Just days before Christmas, Wisconsin justices struck down the state’s GOP-drawn gerrymanders. So far this year, Montana’s supreme court has stepped in to protect voting rights, while a decision in Alabama threatened in vitro fertilization treatments.
In each of these states, unlike at the federal level, voters chose who sits on the bench and which judges get to dictate such profound consequences. And the 2024 elections may now reshape who holds power on supreme courts across the country.
Thirty-three states have elections for their high courts this year; some have as many as five or six seats on the ballot. In total, 82 seats are up for voters to decide.
These races may potentially shift the outcome in high-stakes cases that are already in the legal pipeline on everything from the rules of direct democracy to the fate of reproductive rights.
Michigan and Ohio are the two states where a supreme court’s partisan majority could flip outright. Democrats are defending a narrow edge in Michigan; the GOP is doing the same in Ohio.
But the 2024 elections may also affect the ideological balance of other supreme courts, starting with Kentucky, Montana, North Carolina, and Texas. Some of these states hold nonpartisan races where judicial candidates are not affiliated to political parties; but those courts still tend to have liberal, moderate, and conservative wings, and parties and other groups often get involved in their elections, sometimes pouring in huge amounts of money.
Eighteen states are holding regular elections for their supreme courts, namely races where candidates can challenge incumbent judges or run for an open seat. There are 51 such elections in 2024, but importantly, about a third of them are effectively already over; in most cases, that’s because only one candidate filed to run.
The procedure is markedly different in 15 other states, where incumbent judges who want a new term run in so-called retention elections—simple up-or-down votes, with no challengers, that decide if a judge should stay in office. It is exceedingly rare for justices to be ousted in retention elections—in some states this has never happened—but some do get heated.
You can explore the rules in the state that interests you in our state-by-state guide to each court.
Note that the exact landscape of this year’s elections may still change; if a judge up for retention were to resign early, for instance, it would cancel the election altogether.
The 2024 cycle is already well underway. Three incumbents in Texas were voted out in March in the GOP primary after facing attacks by far-right politicians. An Illinois justice survived a primary. And an Arkansas justice hopped to another seat on the bench to evade retirement rules.
The stakes only escalate from here. Conservatives hope to gain ground on Montana’s liberal-leaning court thanks to the retirement of two justices long targeted by the right. In Kentucky, the retirement of a conservative-leaning justice may have the opposite effect. Democrats risk falling even further behind on North Carolina’s court, while the prospect of Michigan and Ohio’s courts flipping carries important ramifications for sentencing and democracy.
Across Arizona and Florida, four justices who voted to uphold abortion bans this month are up for retention—two in each state. Three justices who took part in the Colorado supreme court’s decision to bar Donald Trump from the ballot also face retention tests. A justice who voted against the erosion of direct democracy faces reelection in Mississippi.
Bolts today guides you through each of the 33 states with elections for their high courts.
Sign up and stay up-to-date
Support us
Bolts is a non-profit newsroom: We rely on donations, and it takes resources to produce this work. If you appreciate our value, become a monthly donor or make a contribution.
States with regular supreme court elections
Alabama
When this supreme court ruled 8-1 in February that frozen embryos are children, endangering IVF treatments, it also brought into full view conservative plans to press for more restrictions on reproductive rights. Five of the court’s nine seats are on the ballot in 2024, but three of the justices who joined that ruling—William Sellers, Jay Mitchell, and Tommy Bryan, all Republicans—are running for reelection unopposed.
The election for chief justice is contested, though. Chief Justice Tom Parker, a far-right jurist whose opinion in the IVF decision drew heavily from the Bible, is retiring. Sarah Stewart, an associate justice on the supreme court who also joined the majority in that ruling, won the GOP primary to succeed Parker and now faces Democrat Greg Griffin in November. Griffin is a lower-court judge who blocked new restrictions on birth centers last year in a victory for reproductive rights groups. No Democrat has won a seat on this court since 2006; last week, the first legislative race since the February ruling swung toward the party.
Stewart’s bid for chief justice means she is not running for reelection for her current seat. Chris McCool, a Republican lower-court judge, is running unopposed and is certain to join the court.
Arkansas
Justice Shawn Womack secured another term without facing any opposition in this state’s March election. But in the two other seats on the ballot, neither incumbent sought reelection. That set up an odd game of musical chairs: Four of the six candidates running for these two open seats were already sitting justices hoping to move to different seats on the court.
As Bolts reported, the perplexing situation is poised to shift Arkansas’ high court further right.
One of these races has already ended: Justice Courtney Hudson, who wanted to change seats to circumvent retirement rules by a few extra years, prevailed over an outsider in March by receiving more than 50 percent of the vote. Hudson now has to resign from her current seat, triggering a vacancy to be filled by Sarah Huckabee Sanders, the state’s conservative governor.
The second race, for the chief justice seat, remains unresolved, but we already know there will be a similar outcome: The only candidate who was not already on the court lost in March. Two sitting justices—Karen Baker and the more conservative Rhonda Wood—grabbed the only spots for the November runoff. Whoever wins that runoff will need to resign from their current seat, handing Huckabee Sanders a second supreme court appointment.
Georgia
Three justices on this supreme court are running for reelection unopposed this year—Michael Boggs, John Ellington, and Nels Peterson. The fourth incumbent seeking reelection this year, Andrew Pinson, faces a challenger: That is itself noteworthy in a state that held 12 consecutive uncontested races for its state supreme court between 2012 and 2018.
Then, in 2020, Democrat John Barrow ended that long streak of uncontested elections by announcing a run to join the court—only to have GOP officials exploit a loophole that wound up outright canceling the election. Barrow sued to make the state hold supreme court elections that year, but his lawsuit was rejected by the very court he hoped to join. In an interview with Bolts two years later, Barrow said the threat that an election may be canceled had a chilling effect on outsiders’ willingness to run for the court. “Anybody who is thinking about running has to run the risk that they pull out the rug from under you,” he said.
Barrow decided to jump back in after all this year. He is challenging Pinson, a former state solicitor general appointed to the court by Republican Governor Brian Kemp in 2022.
Idaho
Chief Justice G. Richard Bevan is certain to secure a new six-year term this year after no one filed to run against him by the March deadline.
Illinois
While Republicans had a real shot at flipping this supreme court just two years ago, Democrats have instead expanded their majority to 5-2. This year, there’s no such suspense: Both justices on the ballot are running unopposed in the general election.
Democratic Justice Joy Cunningham is sure to prevail in the first district, which encompasses Cook County (Chicago). Republican Justice Lisa Holder White, a Republican, will o prevail in the fourth district in western Illinois.
Kentucky
In 2022, a lawmaker with a zealously anti-abortion record failed to win a seat on this court; the result added to Kentucky conservatives’ long standing frustrations, with their effort to secure a reliable conservative majority repeatedly faltering. While Kentucky is now staunchly red, its judicial elections are nonpartisan, and the court’s politics can be difficult to decipher.
This year, conservatives are the ones on the defensive, with Chief Justice Laurance VanMeter—a Republican even if he ran for judge without a party label—retiring and leaving an open seat on the ballot. The race to replace him could shift the court one step to the left. The election won’t be waged statewide; it will only take place within the fifth judicial district, a swing region in central Kentucky. (The district, which includes Lexington and Fayette County, narrowly voted for Trump in 2020 and then for Democrats by a large margin in the 2023 governor’s race.)
The candidates running to replace VanMeter have contrasting political histories. Pamela Goodwine, currently chief judge on the Court of Appeals, has appeared at Democratic events and enjoyed union support; Erin Izzo, an attorney, has spoken at GOP events and is boosted by local conservatives. Abortion is among the issues that may shape the race after a divided supreme court rejected a challenge to Kentucky’s abortion ban last year. VanMeter sided with the majority in that case, which was decided on procedural grounds, and abortion is likely to return to the court in the future.
Louisiana
Scott Crichton, a Republican justice, is retiring, and the contours of the race to replace him are uncertain. The state’s filing deadline is not until this summer, the last in the country. In addition, the state legislature is currently considering options to redraw the state’s judicial map, in part to add a second majority-Black district as many justices have demanded.
Michigan
This is one of the few supreme courts whose partisan majority could flip this year. Democrats currently have a 4-3 majority, an edge that’s come into play in recent cases that touch on sentencing or democracy, and each party is defending one seat this fall.
Democratic Justice Kyra Harris Bolden is seeking to stay on the court, one year after Governor Gretchen Whitmer appointed her. If she wins, it will be enough for Democrats to retain a majority.
Republican Justice David Viviano, meanwhile, is retiring. That gives Democrats a golden opportunity to flip a seat and expand their majority, since they won’t need to oust an incumbent. (Sitting judges typically enjoy a large advantage; in Michigan, while the general election ballot does not list candidates’ party labels, it does mention that they’re incumbents.)
Michigan has a unique system in which the parties nominate their supreme court candidates during a summer convention, rather than in primaries. Besides Bolden, three candidates are running as of publication—a conservative state judge, a Republican lawmaker, and a law professor appointed to a criminal justice task force by Governor Gretchen Whitmer.
Minnesota
Three justices appointed by a Democratic governor—Natalie Hudson, Anne McKeig and Karl Procaccini—must run for reelection this year to stay on the court. While Hudson was just on the ballot in 2022, Governor Tim Walz appointed her chief justice last fall, meaning she must now run to keep that seat. The filing deadline is months away, in June, so these elections have yet to take shape.
But we already know the makeup of the court will change this year. Justice Barry Anderson, who was set to hit the mandatory retirement age in October, said he is resigning in May. Democratic Governor Tim Waltz will appoint a new justice, who won’t face voters until 2026. Meanwhile, Justice Margaret Chutich’s seat was scheduled to be on the ballot this fall; her current term ends in January. But she too announced she is retiring this spring. If she had finished her term and retired as scheduled, the state would have held an open race for her seat this year. Instead, her decision to retire months early means there will be no election for her seat in 2024; Walz will appoint another new justice who also won’t face voters until 2026.
Mississippi
The Mississippi Supreme Court struck down the state’s ballot initiative process in 2021 on a 6-3 vote. All the justices who dissented that day—Robert Chamberlin, Jimmy Maxwell, and James Kitchens—are up for reelection, though Chamberlin and Maxwell are unopposed and already sure to keep their seats on the bench.
But Kitchens, who won his last election with support from state Democrats, faces a crowded field of four challengers, including Republican lawmaker Jenifer Branning.
The fourth and final incumbent on the ballot this year is Justice Dawn Beam, who voted with the majority to void the direct democracy process; she’ll face lawyer David Sullivan.
Montana
Republicans are consolidating power in Montana, but this supreme court remains a hurdle for their priorities. Two weeks ago, the court overturned the Republican attorney general’s effort to stall an abortion rights initiative in a 6-1 vote; days later, in a 4-3 decision, the court struck down four separate Republican laws that had restricted access to voting.
Conservatives failed to change the rules of how justices are elected; two years ago, they failed to oust a Democratic-appointed justice, who went on to write the abortion ruling.
Now, the right has a new shot at gaining ground with the retirements of Justices Mike McGrath and Dirk Sandefur. While the court is nonpartisan, McGrath and Sandefur are former Democratic politicians; McGrath used to be attorney general, and Sandefur won his last race in 2016 against heavy financial involvement from national Republicans. Still, their rulings have sometimes diverged; McGrath authored last week’s voting rights ruling, and extolled the state constitution’s broad protections, while Sandefur harshly criticized McGrath’s analysis in partial dissent. In March, both voted to let the abortion rights measure proceed.
The elections to replace them have each drawn three candidates, several with a history in GOP politics. In each race, the top two in June will move on to a general election in November.
Nevada
Nothing to see in Nevada this year: Justices Elissa Cadish, Patricia Lee, and Lidia Stiglich are all certain to win reelection since no one filed to challenge them by the January deadline.
North Carolina
North Carolina is the poster child for what can happen when a supreme court flips. The GOP won control in 2022, and its new majority promptly reversed decisions on gerrymandering and felony disenfranchisement, and changed gears in racial discrimination cases.
Democrats now hold just two of seven seats, and they’re in danger of slipping further in November since the only seat on the ballot is that of Democratic Justice Allison Riggs. A former civil rights attorney appointed last year by Governor Ray Cooper, Riggs faces Republican Jefferson Griffin, a lower-court judge. Democrats need to defend Riggs’ seat to have a realistic chance of flipping the court back later this decade.
Ohio
The GOP’s majority on this court is just a narrow 4-3, but it became more conservative last year with the retirement of a moderate Republican and the appointment of a conservative prosecutor to the seat. Three seats are on the ballot this year, with two held by Democrats and one by the GOP, so the court could shift in either direction.
Democrats will flip the court if they sweep all three seats, but the GOP would significantly expand its majority if it does the same. Implementation of last year’s referendum protecting abortion rights hangs in the balance, as well as democracy issues such as possible redistricting cases.
All elections are statewide, and the GOP is confident it can take advantage of Ohio’s red lean in the wake of a recent law adding party labels to judicial races. In fact, Republicans are looking to push their advantage with an aggressive play to oust Democratic Justice Melody Stewart: Joe Deters, the GOP justice appointed last year, is challenging Stewart instead of seeking reelection to his own seat.
Meanwhile, Democratic Justice Michael Donnelly will face Republican Megan Shanahan, a lower court judge in Cincinnati. Two lower-court judges, Democrat Lisa Forbes and Republican Dan Hawkins, will face off for the third seat—the one Deters is vacating.
Oregon
Five of Oregon’s seven justices are up for reelection this year. And each and every one of them is running unopposed. With these Democratic-appointed justices all but certain to secure new terms, the court will keep its left-leaning majority.
Texas: Supreme Court and Court of Criminal Appeals
There are six judicial seats on the ballot across the state’s two high courts. All are held by GOP judges, which has won every statewide race since 1994, judicial and otherwise.
Democrats are fielding a candidate in all six—that’s better for them than in 2022—and a confluence of factors may at least give them a shot. For one, the aftershocks of the state’s abortion ban are making judicial politics a bit more salient. Then, there’s the fact that three incumbent Court of Appeals judges were ousted in the GOP primary, an unusual result driven by Attorney General Ken Paxton and his far-right allies’ bid to punish justices who restricted his ability to initiate voter fraud prosecutions. Finally, Supreme Court Justice John Devine, a staunch conservative challenged by Democrat Christine Weems, faces allegations about his ethics.
Still, Texas’ red lean will be difficult for the Democratic candidates to overcome, with Trump expected to again carry the state at the top of the ticket.
Washington
Candidate filing in Washington doesn’t start until May. So it’s still unclear who might challenge the two justices who may run for reelection this year, Steven González and Sheryl Gordon McCloud, both members of the court’s emerging progressive bloc.
But it’s certain that there will be some changeover on the court since Justice Susan Owens is hitting the mandatory retirement age and cannot run for reelection. The state’s judicial establishment has coalesced around Sal Mungia, an attorney who already has endorsements from six sitting justices as of publication.
West Virginia
Charles Trump, a Republican state senator, voted in favor of the state’s near-total ban on abortion in 2022. Now he is certain to join the state supreme court since no one else filed for an open seat by the filing deadline.
The state’s second race also features an unopposed candidate: Justice Haley Bunn, who was appointed to the court by Republican Governor Jim Justice in 2022, drew no challenger. This court was one of the nation’s most polarized last decade, when state Republicans maneuvered to impeach justices or pressure them into resigning to secure a conservative majority.
States that only have retention elections this year
Alaska
Justices Dario Borghesan and Jennifer Henderson, appointed by Republican Governor Mike Dunleavy in 2020 and 2021, face retention tests in November. No Alaska justice has lost a retention race since 1962, despite some organized efforts to oust incumbents in the past.
Still, this court’s membership matters a great deal for the future of reproductive rights. Alaska’s supreme court has ruled in the past that the state constitution protects abortion rights, though it has not revisited that issue since Borghesan and Henderson joined the court, making their views uncertain. State conservatives hope that an anti-abortion majority will emerge on the court and reverse that precedent. The court could soon hear a case filed by Planned Parenthood to expand access to abortion.
Arizona
The two justices who face retention this year, Clint Bolick and Kathryn Hackett King, are both appointees of former Republican Governor Doug Ducey, who expanded the court and loosened constraints on appointment to shift it rightward.
Arizona judges have historically easily prevailed in retention elections, though voters ousted a county judge in 2014, the first time that any Arizona judge had lost in decades, and they ousted three other county judges in 2022. Bolick, who was appointed by Ducey in 2016, received 70 percent in 2018 during his last retention race; King, who was appointed in 2021, has not yet faced voters.
Update (April 10): Both Bolick and King joined a ruling in April that upheld a 1864 law that bans nearly all abortions in the state.
Colorado
Colorado’s supreme court briefly became the center of the political world in December when it ruled that Donald Trump was ineligible to run for president. (The U.S. Supreme reversed the decision in early March.) This year, three of the justices who took part in that decision are up for retention: Monica Márquez, who sided with the majority in that ruling, and Brian Boatright and Maria Berkenkotter, who dissented.
Judicial races are rarely eventful in Colorado—over the last decade, no justice has dipped under than two-thirds of the retention vote—and there’s no high-profile effort to change that in 2024 as of now. Still, Márquez already suffered from one viral false attack in the wake of her vote.
Florida
Florida organizers collected hundreds of thousands of signatures on behalf of two initiatives to protect abortion rights and legalize marijuana, but Attorney General Ashley Moody argued the measures were too unwieldy and confusing and tried to get Florida justices to toss them. That proved too much even for this conservative court, which ruled against Moody this week and placed the measures on November’s ballot.
Only two justices, Renatha Francis and Meredith Sasso, agreed with Moody on both counts, dissenting from both decisions. On the same day, Francis and Sasso also voted to uphold the state’s restrictions on abortion, this time joining a majority to overturn a longstanding precedent.
Francis and Sasso now each face retention elections in November. They were both appointed to the court by Republican Governor Ron DeSantis, and this is their first time facing voters. On paper, the races have the potential to flare up, since abortion and marijuana are popular and high-profile issues. But in practice, no judge has ever lost a retention election in Florida history.
Indiana
Since Indiana adopted a system of retention elections in 1970, voters have never refused to retain a state judge. As of now, there’s no indication that 2024 will break that pattern. The court’s two oldest justices, Mark Massa and Loretta Rush, and its youngest justice, Derek Molter, face retention this fall; all were first appointed to the bench by Republican governors.
Iowa
Justice David May faces voters for the first time since his 2022 appointment by Republican Governor Kim Reynolds, part of a series of appointments with which she’s reshaped the court in her image since signing a law giving herself more authority to decide judicial appointments.
May joined the court just weeks after its landmark opinion ending protections for abortion. The following year, May sided with the anti-abortion camp, voting to reverse a lower-court ruling that had blocked a new ban on abortions after six weeks. Since the supreme court tied that day, the lower court’s decision blocking the ban remained in effect and kept abortion legal in Iowa. But the supreme court is scheduled to weigh in again this year.
Maryland
Six of the seven members on Maryland’s high court were nominated by former Republican Governor Larry Hogan, though all were then confirmed by the Democratic-run Senate. Hogan’s final two nominees, Chief Justice Matthew Fader and Justice Angela Eaves, are up for retention this year, as is the court’s most senior member, Democratic-nominated Justice Shirley Watts. Don’t expect these races to catch fire, since all of the court’s current members who have faced retention races won with at least 75 percent of the vote.
Missouri
Justices Kelly Broniec and Ginger Gooch joined the court last fall via appointments by Governor Mike Parson, a Republican. They each face voters this fall. Retention races have not caught fire in Missouri’s recent past, with justices routinely receiving more than two-thirds of the vote.
Nebraska
Nebraska is one of the few states where justices represent geographic districts. In 2024, only residents of Lancaster County, home to the city of Lincoln and to the state’s first judicial district, get to weigh in on the supreme court, with Justice Stephanie Stacy up for retention for the second time. She cleared her first test back in 2018 with 81 percent of the vote, a share that’s in line with Nebraskans’ history of overwhelmingly retaining their justices; David Lanphier, the last justice in the state who lost a retention election, was ousted in 1996 over some of his rulings, including one that gave dozens of people incarcerated over murder convictions the opportunity for new trials.
New Mexico
New Mexico has an unusual system in which justices run in regular partisan races the first time they face voters, and then in up-or-down retention elections thereafter. Democratic Justice Briana Zamora defeated a Republican just two years ago, 54 to 46 percent. This year, she’s asking voters to retain her for a full eight-year term, typically an easier hurdle for judges to clear.
A high-profile decision in Zamora’s still-brief tenure came in November, when she joined all of her colleagues in upholding the state’s congressional map against a GOP challenge.
Oklahoma: Supreme Court and Court of Criminal Appeals
Across Oklahoma’s two high courts, six judges face retention this year. The group includes four of the state’s five remaining judges appointed by Democratic governors. But this busy schedule is unlikely to provoke fireworks since no Oklahoma judge has ever lost a retention election.
South Dakota
Justice Scott Myren faces his first retention vote, three years after he was appointed to the bench by Republican Governor Kristi Noem. In late 2021, Myren was the only justice to dissent from a ruling that invalidated a 2020 ballot measure legalizing marijuana. A majority of justices said the measure was too broad to fit within a single ballot question, but Myren wrote that the court should be more deferential to voters’ preferences, and described the initiative process as “this bold experiment in citizen-led direct democracy.”
Tennessee
Justice Dwight Tarwater, who joined the supreme court last summer, faces retention in August. After serving as general counsel to Republican Governor Bill Haslam, Tarwater was nominated to the court by Haslam’s successor, Republican Bill Lee. He replaced the court’s last remaining Democratic-nominated justice, cementing the court’s rightward shift; he is one of three justices that Lee has nominated in the past two years, alongside Sarah Campbell, a former clerk of Samuel Alito, and Mary Wagner, a Federalist Society member.
Utah
The Utah supreme court has drawn scrutiny this year for stalling decisions on major cases related to abortion and redistricting. Chief Justice Matthew Durrant, meanwhile, is up for retention. He faced no issue surmounting this test the past two times he faced it, receiving 83 percent of the vote in 2004 and 78 percent in 2014.
Wyoming
Two of the court’s five members, Kate Fox and John Fenn, face voters this year. Both were appointed by Republican governors. Judicial elections in Wyoming have been extremely sleepy affairs over the last two decades; the state’s mandatory retirement age of 70 is far likelier to spark changeover in its membership.
Editor’s note: Information about past retention elections in Arizona has been corrected. The article has also been updated to reflect a ruling on abortion in Arizona that came down shortly after publication.
Sign up and stay up-to-date
Support us
Bolts is a non-profit newsroom that relies on donations, and it takes resources to produce this work. If you appreciate our value, become a monthly donor or make a contribution.