The Winding Road to Ending ICE Collaboration in Raleigh
Donnie Harrison was an immigration hardliner during his long tenure as Wake County Sheriff, until he was swept out of office by pro-immigrant activism during the Trump years. Now he’s seeking his old job back.
Jeffrey Billman | August 26, 2022


This article is part of a series on how the midterms may reshape immigration policy. Read our other installments on Frederick County, Maryland, and Barnstable County, Massachusetts (Cape Cod).
Update: Willie Rowe beat Donnie Harrison on Nov. 8, 2022.
A week before Donald Trump clinched the Republican presidential nomination in May 2016, 13-year-old Alex Matehuala asked Wake County Sheriff Donnie Harrison to cut his office’s longstanding ties with Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE). Standing in a church in downtown Raleigh, North Carolina, in front of nearly 100 people, most of Central American descent, Alex told Harrison that his schoolmates worried every day that their parents would be taken before they got home.
“Will you continue to renew a racist program that puts families at risk of being separated?” he asked.
The 287(g) program, which Harrison joined in 2007, authorized local deputies to check the immigration status of people they arrested—a job that’s usually the purview of federal authorities—and detain suspected undocumented immigrants after they’d otherwise be released. Over the previous two years, it had led to more than 1,000 deportations, according to data compiled by Appalachian State University sociologist Felicia Arriaga. It had also spread fear among immigrant communities: a low-level traffic infraction could easily escalate into deportation proceedings.
But Harrison said he saw no reason to end the program. In 2016 and 2017, ICE deported another 498 people from Wake County through 287(g), according to Arriaga.
“I have been in forums with [Harrison] where community members have literally been crying. Their families have been torn apart by having a loved one deported for a very low-level offense, getting flagged through 287(g) and leaving their kids behind,” Angeline Echeverría, the former director of El Pueblo, the Latinx advocacy organization that sponsored the 2016 event, told Bolts this month. “Just, like, terrible, devastating stories. And Donnie was not moved.”
Ahead of the 2018 midterms, with Trump’s immigration policies rattling the nation, local law enforcement agencies’ cooperation with ICE came under intense scrutiny. In North Carolina, that dynamic put several sheriffs in the hot seat—including Harrison, a Republican who hadn’t faced a serious challenge since becoming sheriff in 2002 despite Wake County trending Democratic.
Harrison lost by 10 points to Gerald Baker, a former deputy who pledged to withdraw Wake County from 287(g) and made good on his word after taking office. Harrison wasn’t alone in defeat. Six of North Carolina’s most populous counties—also, Mecklenburg (Charlotte), Guilford (Greensboro), Forsyth (Winston-Salem), Buncombe (Asheville), and Durham—elected new Black Democratic sheriffs who vowed to restrict collaboration with ICE.
Four years later, Harrison wants his job back and he is on the ballot in November’s sheriff election. During the Republican primary, he reiterated his support for 287(g). After he won the nomination in May, the immigrant-rights activists who helped oust him in 2018 geared up for another fight—this time in a very different environment. There was no blue wave on the horizon, and immigration no longer drove headlines. Baker, meanwhile, lost the Democratic primary amid allegations of mismanagement, cronyism, low morale, and criticism of his aggressive but ineffective response to the protests that followed George Floyd’s murder. Harrison’s new opponent, former deputy Willie Rowe, lost to Harrison by 18 points in the 2014 sheriff’s race. Even in a county Trump lost twice by double digits, advocates feared that if 287(g) flew under the radar, Harrison could stage a comeback.
But on Aug. 17, Harrison’s campaign made an abrupt reversal. In a statement provided to Bolts, Harrison said that if elected, he would no longer participate in 287(g) or honor ICE detainers—requests that sheriffs continue detaining someone beyond their scheduled release time in order to give ICE time to pick them up. A consultant for Harrison’s campaign also said he would recognize Community Action IDs—alternative identification cards for immigrants who cannot obtain state IDs—which he’d previously rejected but Baker began recognizing earlier this year.
“Mr. Harrison fully understands the concern many residents and citizens have about the 287(g) program targeting specific races and nationalities,” Brad Crone, the consultant, told Bolts in an email. “There are better ways to address public safety concerns by extending criminal checks for all people who are processed into the detention center.”
Immigrant-rights advocates are skeptical about Harrison’s change of heart. “Because of the administration that he ran before, I don’t quite believe it,” Arriaga said. “It feels like there’s gonna be something else, and I’m scared of what that something else would be.”
“I’ve certainly heard of candidates positioning themselves in a certain way in primaries and then shifting to the center for the general election, thinking they need to appeal to a broader constituency,” Echeverría added. “I have never seen it this dramatically in a local election in Wake County. This is a huge about-face.”
Harrison might be attempting to neutralize a contentious issue as he seeks to win back the sheriff’s office—Rowe has already promised not to rejoin 287(g). But Echeverría says his record of pushing immigration enforcement while dismissing the community’s concerns about ICE collaboration speaks volumes.
“Any reporter looking into his record can see that he consistently renewed the 287(g) agreement when he was sheriff,” she said. “He was not persuaded at all by community members whose lives were upended by the program and whose families were separated. So it’s just—I mean, I guess people have short memories.”
Harrison was always an immigration hardliner. He was the first sheriff in North Carolina to enroll in Secure Communities, in which local police run the fingerprints of every person they arrest through a national database to determine their immigration status. Harrison said the program would help his office “find more criminals or criminal aliens who otherwise could have slipped through the cracks.” In its first two years, nearly two-thirds of Secure Communities deportees from Wake County hadn’t been convicted of a crime. (President Joe Biden halted Secure Communities after taking office.)
In November 2007, the Wake County Board of Commissioners agreed to hire 12 deputies to implement 287(g), which cost about $539,000 a year to operate. By 2009, eight North Carolina counties and the city of Durham had entered into 287(g) agreements as well, with sheriffs falsely blaming immigrants for rising property and violent crime rates.
Sometimes, overt racism bubbled to the surface. One sheriff complained about “trashy” Mexicans “breeding like rabbits.” Alamance County Sheriff Terry Johnson told his deputies to “go out there and get me some of those taco eaters.” (In 2012, the U.S. Justice Department sued Alamance County for targeting Latinos. Its sheriff’s office was forced to withdraw from 287(g), though Alamance joined the program again during the Trump administration.)Harrison’s participation in 287(g) didn’t create roadblocks to reelection in 2010 and 2014. Echeverría says El Pueblo and other immigrant advocacy groups didn’t coalesce into a political force until 2015, when Republican Governor Pat McCrory signed a law that prohibited sanctuary cities and banned government agencies from using consular or embassy documents to verify a person’s identity.


Trump’s immigration policies further moved the issue at the forefront of the nation’s preoccupations, especially in urban counties like Wake, which voted for Hillary Clinton by more than 20 points. Harrison nevertheless argued that his close ties with the least popular federal agency made the county safe. “If I turn a child molester or a bank robber loose, or whatever on the street, and I turn him loose because I didn’t know who he was and he went down the street and robbed a bank or molested a child, who’s going to be blamed for it?” Harrison said in 2018.
A study of North Carolina from the libertarian Cato Institute found “no statistically significant impact of 287(g) program participation on either violent or property crime rates.” In addition, most people ensnared by 287(g) were sitting in jail pretrial and over misdemeanor charges, including minor offenses such as driving without a license or with a broken taillight.
Baker made 287(g) central to his 2018 campaign, promising to leave the program “for the sake of humanity.” The issue drew national attention and financial investments. The ACLU ran ads in Wake County that highlighted 287(g) and criticized Harrison’s support for a deputy who was involved in an assault on an unarmed Black man.
Echeverría says that when Baker severed ties with ICE, many in the Latino community were “very excited that there’s an elected official who said he was going to do something positive for the community and actually did it.” When Baker began recognizing Community Action IDs earlier this year, “that probably made it more tangible and more real.”
Ending 287(g) was “a local issue that’s tied to a national issue,” Echeverría said. “And the national apparatus was horrific at that time. So it couldn’t fully give the relief that community members would want. But it definitely made a difference.”
Activists notched a victory “at a time when, honestly, a lot of the policy advocacy on the state level and on the federal level was going nowhere,” she added.
But ICE pushed back. After Baker and other new North Carolina sheriffs terminated 287(g) and stopped honoring detainer requests, ICE retaliated by conducting a wave of raids in North Carolina, which it called the “direct result of some of the dangerous policies that some of our county sheriffs have put into place.”
Under Trump, ICE also tried to expand its reach, though participation in 287(g) remains rare: Fewer than 150 of the nation’s roughly 3,000 counties have joined, including just 14 of North Carolina’s 100 sheriffs. (All state sheriffs are up this year.) Of them, 13 hail from rural counties Trump won handily. The exception is Nash County, which narrowly backed Biden. There, GOP Sheriff Keith Stone, who signed onto 287(g), faces Democrat David Brake in November. (Brake did not respond to Bolts’s request for comment.)
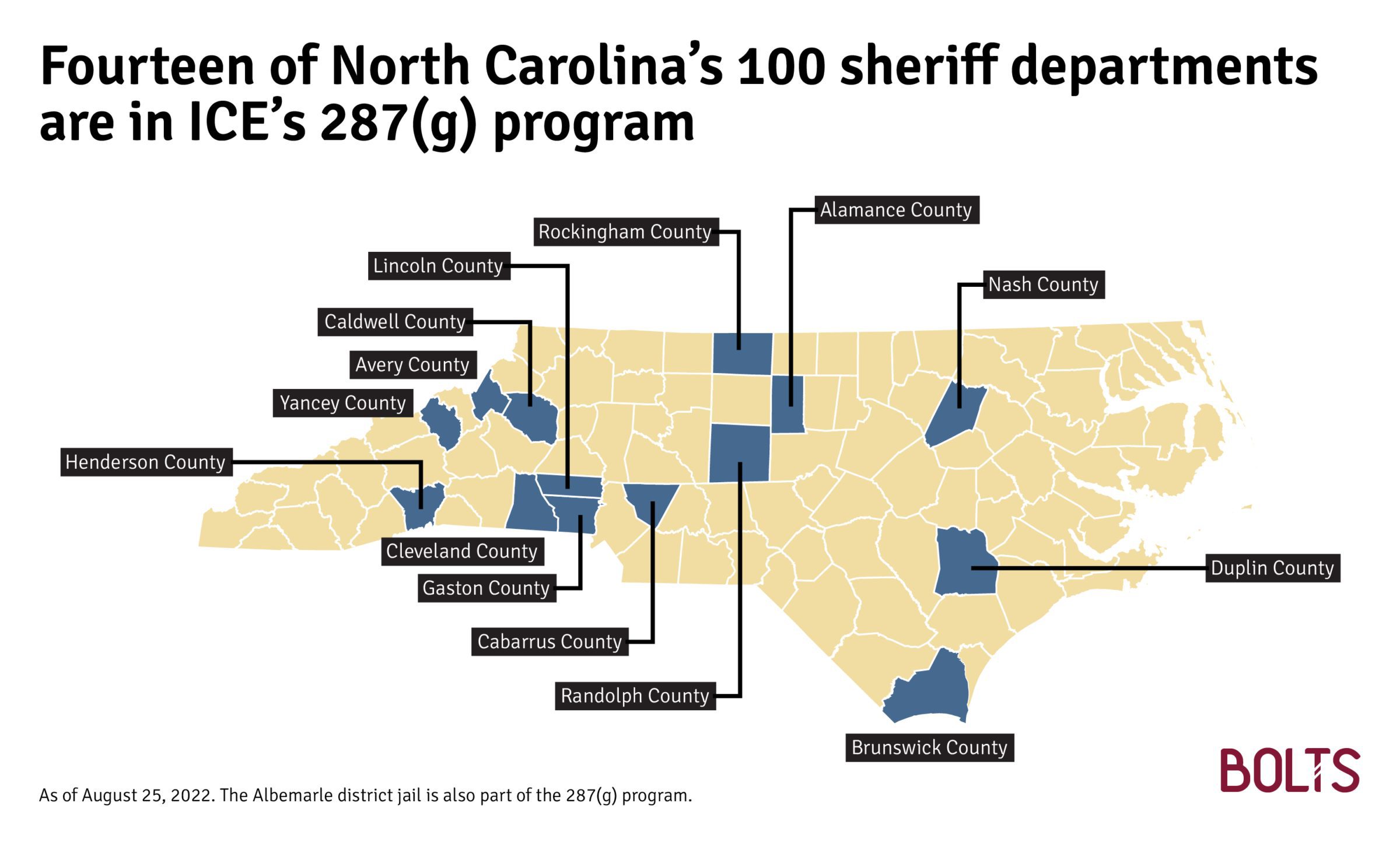

These 14 counties’ combined population is far smaller than those of Wake and Mecklenburg (Charlotte), which quit 287(g) after the 2018 midterms. Mecklenburg County Sheriff Gary McFadden is running unopposed for reelection in November.
Those 2018 results reflected a new political reality: In many urban areas in North Carolina and across the country, partnering with ICE is untenable.
That hasn’t sat well with Republican-led legislatures. Florida passed laws requiring local law enforcement to honor ICE detainers and participate in 287(g) by 2023. Texas and Tennessee required local police to honor detainers in 2017 and 2018, respectively. Arkansas and Mississippi banned so-called sanctuary cities. Twice in the last four years, North Carolina Republicans passed bills mandating that law enforcement honor ICE detainer requests. Governor Roy Cooper, a Democrat, vetoed both. But in November, the GOP hopes to pick up enough legislative seats to claim supermajorities that can override Cooper’s vetoes.
“I assure you I can come in and in a short amount of time put things back on track,” Harrison told a candidate forum in April, three weeks before the primary. The sheriff’s office had a critical staffing shortage, he said. Fentanyl was epidemic. Gun violence was rampant. Harrison promised to make the county safe.
That included working with ICE. Asked point-blank during the forum if he would reinstate 287(g), Harrison responded, “Yes. I will do whatever it takes to keep you safe.”
“I can tell you, 287(g), people don’t understand it, didn’t understand it,” the former sheriff continued. “I don’t have time to tell you now other than the fact that if you get arrested and you come to the jail, then they found out that you were illegal, or you were not legal, then they can take over as far as what will happen after that. I would not want a sex offender living in my neighborhood. And I can tell you this, the people that I talk to like the 287(g).”
But he also said he didn’t think 287(g) would exist by the time the new sheriff takes office in December. Crone, Harrison’s consultant, told Bolts that a key factor in Harrison’s reversal on 287(g) was his belief that Biden plans to kill the program by the end of the year.
It’s not clear where that idea came from. While Biden promised during the presidential campaign to end 287(g) agreements forged during the Trump administration, his administration has made few moves in that direction—to the chagrin of his allies.
Another factor appears to be political necessity. No Republican has won a countywide contest since 2014, the last year Harrison won the sheriff’s office. In 2018, he outperformed every other Wake Republican but still lost by double digits. Harrison entered the general election this year with big advantages in money and name recognition over Willie Rowe, Harrison’s Democratic opponent. But Wake County’s blue lean still makes him an underdog, says Michael Bitzer, a political scientist at Catawba College in Salisbury, North Carolina, and an expert on the state’s voting patterns.


“You can put up the best Republican ideal candidate, and I think voter loyalty and behavior is still going to matter when it comes to this kind of dynamic,” Bitzer said.
Harrison couldn’t afford to let the election become a referendum on 287(g). “He wants to win,” said Rowe. “That’s the motivating factor. The numbers aren’t there to support that kind of policy.”
Even so, Harrison’s campaign didn’t equivocate about his new positions. Crone said that Harrison would not rejoin 287(g) even if the next president pushes to expand the program. He does not believe it’s necessary, Crone said. Everyone entering the jail will be screened to verify their identity and to look for outstanding warrants or see if they are wanted in another jurisdiction.
Harrison’s new stance on detainer requests—he won’t honor one without “a warrant signed by a magistrate or judge,” Crone said—is also arguably more categorical than Rowe’s.
Rowe told Bolts that he believes detainers violate the Fourth Amendment. However, he said that he would honor them as a “last resort” to keep people accused of violent crimes behind bars, but only after first asking the DA and courts to raise their bonds. “That’s the legal way to do it,” Rowe said.
Some critics question whether Harrison’s election-year conversion is genuine. “You can say anything to get the vote,” Rowe said. “But the proof in the pudding is when it comes time to put it into practice—what are any loopholes to get around? I can say, every time I work with immigrants, ‘Well, they’re a threat.’ And that word is used so much in dealing with so many people. You just say, “They’re a threat, and this is why I’m taking this course of action.’”
Iliana Santillán, the current director of El Pueblo, remained skeptical but said she’s “hopeful he’d maintain his promise if elected but am reminded once again of the hundreds of families separated during his time as Wake County Sheriff from 2002 to 2018.”
*This story was updated with comments from Santillán.

